What is Sleeping/Awaiting Command Session
A session with the status of Sleeping/awaiting command is simply client connection with no active query to the sql server.The table below shows transitions from "running" to "sleeping" states for a session.
The question usually around a session that is holding locks and its state is sleeping/Awaiting command.If the client has a open transaction and the client did not submit Commit or Rollback command the state is showing as Sleeping/Awaiting command.
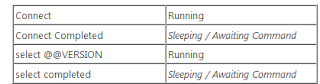
We can examine this by running the below query. Open a new query window in AdventureWorks database. And run the below query.
Now go to another window run the below query and see the state. It is in Sleeping mode.
Giving some more in depth explanation about :
A thread is using the CPU (called RUNNING) until it needs to wait for a resource. It then moves to an unordered list of threads that are SUSPENDED. In the meantime, the next thread on the FIFO (first-in-first-out) queue of threads waiting for the CPU (called being RUNNABLE) is given the CPU and becomes RUNNING. If a thread on the SUSPENDED list is notified that it’s resource is available, it becomes RUNNABLE and is put on the bottom of the RUNNABLE queue. Threads continue this clockwise movement from RUNNING to SUSPENDED to RUNNABLE to RUNNING again until the task is completed. You can see processes in these states using the sys.dm_exec_requests DMV.
The question usually around a session that is holding locks and its state is sleeping/Awaiting command.If the client has a open transaction and the client did not submit Commit or Rollback command the state is showing as Sleeping/Awaiting command.
We can examine this by running the below query. Open a new query window in AdventureWorks database. And run the below query.
Now go to another window run the below query and see the state. It is in Sleeping mode.
Giving some more in depth explanation about :
A thread is using the CPU (called RUNNING) until it needs to wait for a resource. It then moves to an unordered list of threads that are SUSPENDED. In the meantime, the next thread on the FIFO (first-in-first-out) queue of threads waiting for the CPU (called being RUNNABLE) is given the CPU and becomes RUNNING. If a thread on the SUSPENDED list is notified that it’s resource is available, it becomes RUNNABLE and is put on the bottom of the RUNNABLE queue. Threads continue this clockwise movement from RUNNING to SUSPENDED to RUNNABLE to RUNNING again until the task is completed. You can see processes in these states using the sys.dm_exec_requests DMV.




Comments