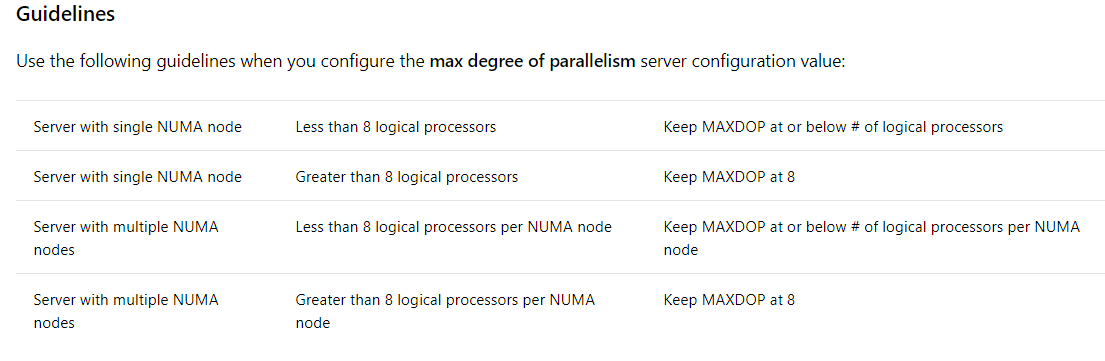
MAXDOP recommendation
This topic describes how to configure the max degree of parallelism (MAXDOP) server configuration option in SQL Server 2017 by using SQL Server Management Studio or Transact-SQL. When an instance of SQL Server runs on a computer that has more than one microprocessor or CPU, it detects the best degree of parallelism, that is, the number of processors employed to run a single statement, for each parallel plan execution. You can use the max degree of parallelism option to limit the number of processors to use in parallel plan execution. SQL Server considers parallel execution plans for queries, index data definition language (DDL) operations, parallel insert, online alter column, parallel stats collection, and static and key-set-driven cursor population.
To enable the server to determine the maximum degree of parallelism, set this option to 0, the default value. Setting maximum degree of parallelism to 0 allows SQL Server to use all the available processors up to 64 processors. To suppress parallel plan generation, set max degree of parallelism to 1. Set the value to a number from 1 to 32,767 to specify the maximum number of processor cores that can be used by a single query execution. If a value greater than the number of available processors is specified, the actual number of available processors is used. If the computer has only one processor, the max degree of parallelism value is ignored.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/configure-windows/configure-the-max-degree-of-parallelism-server-configuration-option?view=sql-server-2017


Comments